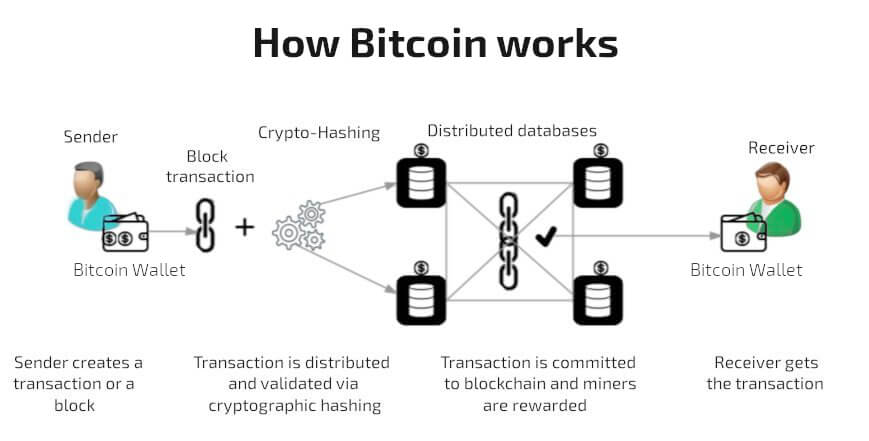
In an era increasingly defined by digital transformation, few innovations have captured the global imagination—and sparked as much debate—as Bitcoin. Conceived in 2008 by an enigmatic entity known only as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin introduced a radical concept: a digital currency free from the oversight of central banks, governments, and financial institutions. It was designed to be peer-to-peer electronic cash, enabling direct transactions between users without the need for intermediaries. This foundational principle of decentralization is not merely a technical detail; it is the philosophical core that underpins Bitcoin’s revolutionary appeal and its promise of a more open, equitable financial future.

At the heart of Bitcoin’s ingenious architecture lies the blockchain, a shared public ledger that meticulously records every single Bitcoin transaction ever made. Imagine a continuously growing list of records, or 'blocks,' each cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming an unbroken 'chain.' When a transaction occurs—say, sending Bitcoin from one wallet to another—it is bundled with other recent transactions into a new block. This block is then added to the end of the chain, creating an immutable and transparent record visible to all participants in the network. This distributed ledger ensures that every Bitcoin wallet can accurately calculate its spendable balance, providing a robust system for verifying ownership and preventing fraudulent double-spending.
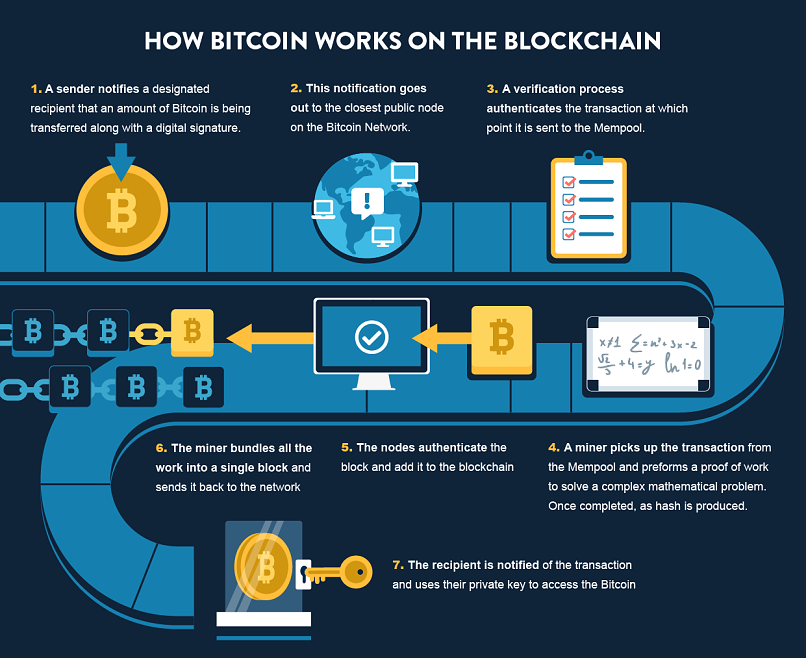
But how are these transactions verified and new blocks added to this ever-expanding chain? This is where 'mining' comes into play. Bitcoin mining is a sophisticated, distributed consensus system where powerful computers, known as miners, compete to solve complex computational puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block of verified transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees. This process not only confirms pending transactions but also secures the network against manipulation, making it incredibly difficult to alter past records. While transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain, the identities of the participants remain pseudonymous, linked only by their unique wallet addresses, which can be generated anew for each transaction to enhance privacy.
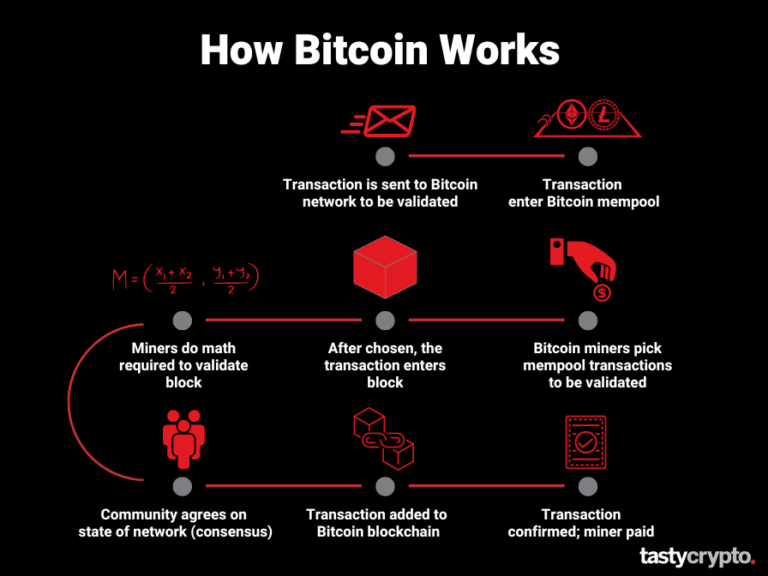
Bitcoin is more than just a digital currency; it represents a paradigm shift in our understanding of value, trust, and ownership in the digital age. Its underlying technology, the blockchain, has inspired an entire ecosystem of decentralized applications and cryptocurrencies, laying the groundwork for what is often called Web3. While its volatility and scalability remain subjects of ongoing discussion, Bitcoin’s enduring presence and increasing adoption by institutions and individuals alike underscore its profound impact. It continues to challenge traditional financial models, offering a glimpse into a future where monetary control is distributed, transparent, and potentially, more democratic.